Functional capacity shows a decline with the senescence process (aging), reaching a reduction greater than 40% between 60 to 90 years of age, this decline may be associated with many factors, such as decreased strength, power and muscle mass. These declines are associated with increased risk of falls and fractures, decreasing quality of life and […]
During the process of senescence (aging), physical capacities such as muscle strength, cognitive functions such as memory gradually diminish. Structural changes happen in the brain as a decrease in the hippocampus and gray matter in the frontal lobe causing a cognitive decline. Whereas a decline in white matter volume in the prefrontal cortex (PF) is […]
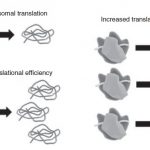
Muscle hypertrophy is one of the best known adaptations to strength training (ST), used as a strategy against muscle atrophy caused by aging or chronic diseases. The molecular mechanisms of this process are not yet well understood and understood. The study brought recent molecular mechanisms for such adaptation, deepening the function and ribosomal biogenesis. Increased […]
Applying or training strength (ST) near muscle failure and at a high level of effort is required to optimize training results, a limitation of the practice of training until the moment of muscle failure is safety, especially when training with pounds bars and away from a mate. Some strategies have been adopted to estimate the […]
The aging process, even without chronic disease, is associated with a variety of biological changes that contribute to decreased muscle mass, bone mass, strength, power, and function, leading to catastrophic events such as falls and fractures. This process is also known as sarcopenia, where it involves decreasing the above mentioned items. Above 60 years of […]
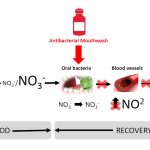
After acute exercise, blood pressure values are reduced compared to pre-exercise values. This phenomenon is known as post-exercise hypotension (PEH), being an important physiological adaptation in the treatment of hypertension in hypertensive people. One of the mechanisms for HPE is the increased activity of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells, increasing endothelial nitric oxide (NO) […]
Decline in physical fitness, glucose control, and insulin sensitivity (SI) are predictors of disease and all-cause mortality. Loss of physical fitness with the senescence process is associated with lower mitochondrial protein synthesis, abundance, respiration, and a high emission of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Cardiorespiratory exercise is an appropriate approach when aiming to increase physical fitness […]
Strength training (ST) is performed at different intensity levels from the beginning to the end of the exercise series, increasing the sensation of exertion as the exercise progresses to more vigorous levels, usually leading to changes in facial expression of ST practitioners. It is possible that the change in facial expression may be used as […]







 Português
Português Español
Español